What Are The Types Of Ductwork?
Even though it provides one of the most crucial functions, ductwork is the component of the HVAC system that we sometimes overlook. Without air ducts, the rest of the HVAC system would be worthless since they are the conduits used to distribute warm or cooled air throughout the structure. In a house or business structure, there are a few various types of air ducts that may be employed, and each one has benefits and drawbacks of its own. Your HVAC requirements will dictate the kind of ductwork you should employ, which may be decided by an HVAC expert. Flexible, stiff, and semi-rigid ducting systems are the three primary categories. The application, layout, and design specifications will determine the sort of system employed. Each method has benefits and drawbacks. To properly install a ductwork system, it is essential to comprehend the distinctions between each type of ducting system.
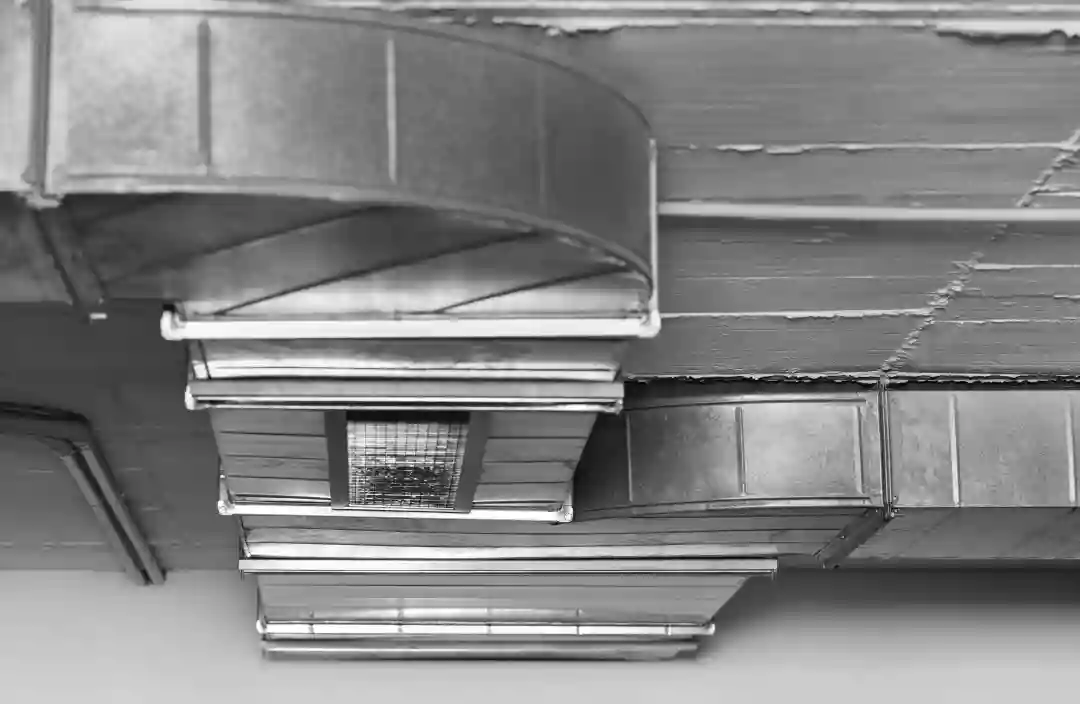
Round, Oval And Rectangular
Buildings are heated and cooled effectively by the use of ducts that are concealed under walls, floors, and ceilings. Air ducts often come in three different shapes: oval, round, and rectangular. Each form has unique benefits and drawbacks. The most typical ducting form seen in homes is round. Due to their simple assembly, round ducts use less material and may be installed fast. Due to these reasons, installing circular ductwork is sometimes the most affordable option. Friction is decreased by increased airflow via rounded surfaces. When HVAC systems are operating, this characteristic lessens noise pollution. Round ductwork's main drawback is the height constraints associated with its installation.
Square or rectangular ductwork is utilised when there is a lack of space. Although rectangular ducting requires more material, the shape offers a larger airflow volume. This enhanced airflow is a significant benefit for HVAC systems with low pressure. Rectangular ducting is also visually pleasant when it is exposed in commercial or renovated areas. More noise pollution is produced by vibration in rectangular ductwork than in round or oval ducts. Contrary to other forms, connections in rectangles are not as smooth. Leaks and inadequate connections within the ducting can cause energy loss.
Round and rectangular ducts' greatest features are combined in oval ducting. Oval duct systems are extremely effective, even though they are less prevalent than other designs. They have a low profile, high flow, and curved surfaces to lessen noise pollution. Oval ductwork has smooth connections, which helps keep it waterproof.

Need assistance finding ductwork cleaning near you?
Get a QuoteFlexible Ductwork
Typically, flexible ducts are cylindrical tubes formed of steel wire helixes that are wrapped in pliable yet resilient plastic. The majority of flexible ducts also have insulation around them to maintain the air within at the proper temperature. The cheapest and easiest to install ducts are flexible ones. In places where stiff ductwork would be too challenging to install, flexible ducting is the ideal type to utilise. These flexible air ducts can bend around stationary objects to fit practically any area. Flexible ducts may kink and bend, though, which can reduce airflow and the effectiveness of the HVAC system.
The ridges inside the ducts might also somewhat impede airflow. Flexible ducts are typically cylindrical tubes made of steel wire helixes that are covered with supple yet durable plastic. To keep the air within flexible ducts at the right temperature, most of them also have insulation surrounding them. Flexible ducts are the least expensive and most convenient to install. Flexible ducting is the best type to use in locations where installing rigid ductwork would be too difficult. These adaptable air ducts can flex to suit almost any space and can be bent around stationary objects. However, kinks and bends in flexible ducts can limit airflow and the efficiency of the system. Additionally, the ridges inside the ducts may somewhat obstruct airflow.
Rigid Ductwork
Rigid ductwork is the second kind of ducting. Rigid ducts come in both rectangular and cylindrical shapes, and they come in a variety of sizes and materials. The ducts' rigidity eliminates the possibility of kinks or bends obstructing airflow, and unlike flexible ducts, they are impervious to tearing or punctures. Rigid ducts, however, cannot be employed with ease in tight locations. The three primary forms of rigid ducting are fibreboard, fiberglass-lined, and sheet metal ducts. Sheet metal ducts are commonly made of either galvanised steel or aluminium.
Aluminium ducts are lightweight and easy to erect. Due to their nonporous nature, sheet metal ducts and flexible ducting are mould-resistant, providing excellent air quality for a longer length of time. This type of ductwork is the most durable since it can keep its shape and resist being easily crushed. Compressed fibreglass fibres that have been sealed to keep airborne particles out make up fibreboard. Ducts made of fibreboard are excellent insulators on their own and don't need extra insulation. Additionally, they are the most affordable to install of all duct types.
Semi-Rigid Ductwork
Semi-rigid ductwork, which is regarded by many as the most trustworthy form of duct for ventilation, offers a ventilation system with no chance of leaks when placed properly. Since semi-rigid ducts are often erected more quickly than rigid ducts, labour expenses are reduced. The shape of some semi-rigid duct designs may be changed from round to oval without sacrificing effectiveness. Even when height is limited, installers may still create effective systems because of this attribute. Modern, spotless, leak-free, and simple to install is semi-rigid ducting intended for household ventilation systems. It is an alternative to the standard method of using solid plastic ducting to distribute air throughout a house. The radial technique used by semi-rigid, in contrast, allows for lower duct diameters, which makes it much simpler to fit into compact areas, especially when combined with duct flexibility.
In this article: