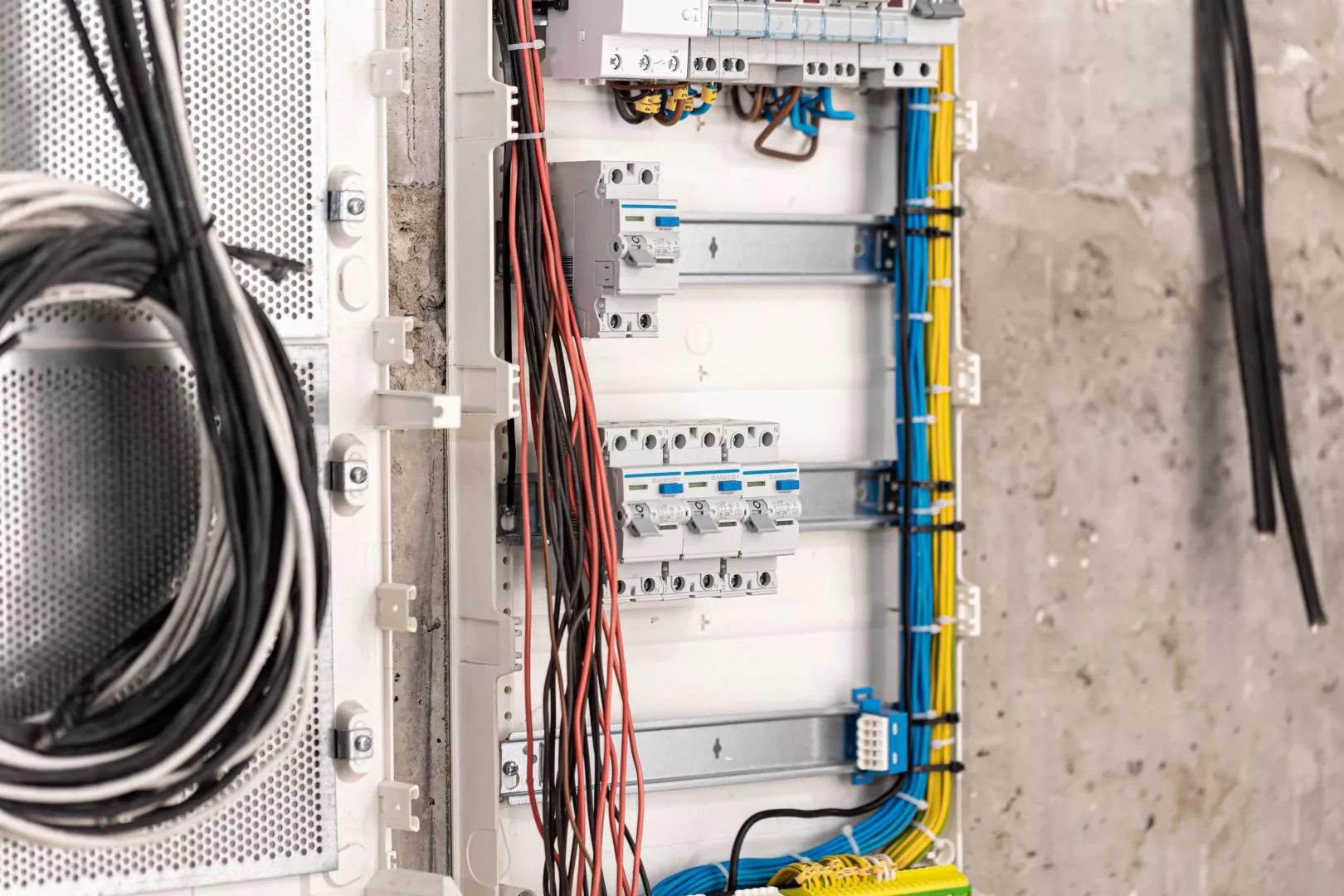
Faulty Wiring and Electrical Overloads
Faulty Wiring and Electrical Overloads
One common cause of power outages at home is faulty wiring. Faulty wiring means the electrical wires in your home are damaged, loose, or not connected properly. This can make it difficult for electricity to flow safely, leading to power disruptions or even hazards like sparks or fires. Older homes with outdated wiring are particularly at risk, as insulation around wires can wear out over time, increasing the chances of short circuits.
Another issue that can lead to power outages is electrical overloads. This happens when too many appliances or devices use electricity at once, putting excessive strain on the system. If the circuit is overloaded, it may cause the breaker to trip or, in severe cases, lead to overheating and fires. Common causes include using multiple high-power devices like washing machines, microwaves, and heaters on the same circuit.
To prevent these issues, regular inspections by a qualified electrician are essential. They can identify and fix faulty wiring before it becomes a major problem. Homeowners should also be mindful of how many high-wattage appliances they use simultaneously. Using surge protectors, spreading loads across different circuits, and upgrading an outdated panel help maintain a stable power supply and reduce outages.
Issues with the Circuit Breaker
A circuit breaker plays a crucial role in protecting your home’s electrical system by shutting off power when it detects a problem. However, when circuit breakers malfunction or experience issues, they can cause unexpected power outages. Understanding the common causes of breaker problems can help you prevent disruptions and maintain a safe electrical system.
Tripped Breakers
One of the most common issues is a tripped breaker, which happens when too much electricity flows through a circuit. Overloading occurs when multiple high-power appliances, such as heaters, microwaves, or washing machines, are running at the same time. When this happens, the breaker shuts off the power to prevent overheating and potential electrical fires.
Loose Connections
Over time, circuit breakers and wiring connections can become loose due to wear and tear. Loose connections can cause flickering lights, power fluctuations, or unexpected outages. This issue can also lead to overheating, which may pose a fire hazard. Regular electrical inspections can help detect and fix loose connections before they become dangerous.
Breaker Failure
Circuit breakers, like all electrical components, can wear out over time. If a breaker fails, it may not trip when necessary, leaving your home vulnerable to electrical surges and short circuits. Alternatively, a faulty breaker may trip too often or fail to reset properly. If you notice frequent power issues, a professional electrician should inspect and replace the breaker if needed.

Need assistance finding electrical repairs near you?
Get a QuotePower Grid Failures and Utility Issues
The power grid delivers electricity from power plants to homes and businesses. When problems occur, large-scale outages can affect entire areas. These failures can result from technical malfunctions, extreme weather, or high electricity demand.
Extreme weather is a major cause of grid failures. Storms, high winds, flooding, and lightning can damage power lines and substations. In winter, heavy snow and ice may break power lines, while summer heat can overload the grid as air conditioning use spikes.
Equipment failure within the power grid is another issue. Transformers, substations, and transmission lines require maintenance, and when components fail, outages can spread. Aging infrastructure struggles to handle rising energy demands.
Sometimes, the grid becomes overloaded, especially during extreme weather. If demand exceeds supply, utility companies may use rolling blackouts to stabilise the system, temporarily cutting power to certain areas.
If a power outage occurs due to a grid failure, contact your electricity provider for updates. Utility companies work to restore power quickly, but widespread outages may take hours or days. Backup power sources like generators can help during extended outages.
Faulty Electrical Components
Faulty electrical components can cause power outages, electrical hazards, and even fires. Over time, plugs, sockets, switches, and wiring can wear out or become damaged, leading to poor connections and unreliable power. Frayed wires, loose connections, and overheating components may trip the circuit breaker or cause sudden electrical failures.
Plugs and sockets are common problem areas. Loose or damaged sockets can cause intermittent power loss, overheating, or sparks. If a plug feels loose in an outlet or shows scorch marks, it may need replacing. Similarly, outdated wiring can lead to flickering lights, power surges, or unexpected outages.
Malfunctioning appliances can also cause electrical failures. A faulty device may create a short circuit, triggering the breaker to shut off power. Appliances that overheat, make unusual noises, or trip breakers frequently should be checked or replaced.
Ignoring faulty electrical components can lead to electric shocks and fire hazards. Regular inspections and timely repairs help prevent serious issues. If you notice flickering lights, buzzing outlets, or overheating plugs, consult a qualified electrician to ensure safety and reliability.
Storms and External Damage
Severe weather conditions and external damage are major causes of power outages. Strong winds, heavy rain, snow, and lightning can affect power lines, transformers, and substations, leading to temporary or prolonged electricity loss. Homes in areas prone to storms or extreme weather should take preventive measures to reduce the impact of these outages.
Strong Winds and Falling Trees
High winds can bring down power lines, damage utility poles, and even cause trees or branches to fall onto electrical infrastructure. When trees or debris hit power lines, they can sever connections or create electrical faults, resulting in widespread outages. Keeping trees trimmed near power lines can help reduce this risk.
Heavy Rain and Flooding
Excessive rainfall and flooding can damage underground cables and electrical substations. Water can seep into electrical equipment, causing short circuits and increasing the risk of power failures. In some cases, flooding can also weaken the ground around power poles, making them unstable and more likely to fall.
Snow, Ice, and Freezing Conditions
Winter storms bring snow and ice, which can weigh down power lines, causing them to sag or break. Ice accumulation on trees can also make branches snap and fall onto power lines, cutting off electricity. Freezing temperatures can further impact transformers and substations, making power restoration more difficult.
Lightning Strikes
Lightning strikes can directly hit power lines, causing electrical surges that damage transformers and household appliances. These surges can travel through the grid, leading to sudden power loss. Installing surge protectors can help protect electrical devices from damage during storms.
Protecting Your Home
While storms and external damage are often unavoidable, precautions can help minimise their effects. Keeping trees trimmed, securing outdoor items before storms, and using surge protectors can reduce risks. If a power line is damaged near your home, stay away and report it to your utility provider for safe repairs.
In this article: